Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter searches for evidence that water persisted on the surface of Mars for a long period of time.
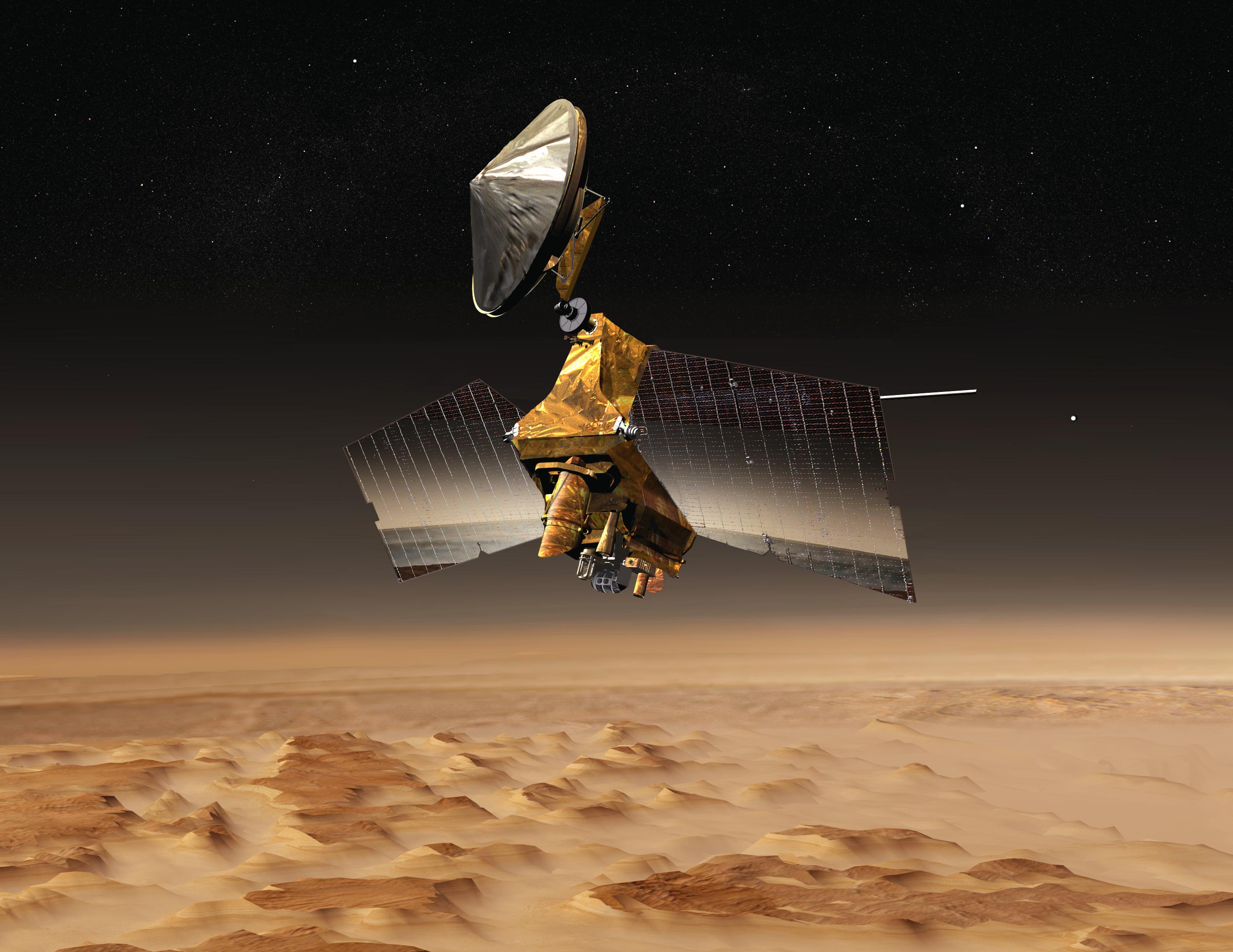

Meet the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
Key Facts
Launch | August 12, 2005 |
Launch Location | Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida |
Cruise | August 2005 - March 2006 |
Mars Orbit Insertion | March 12, 2006 |
Weight | 4,806 pounds (2,180 kilograms) at launch, including fuel |
Electrical Power | Solar panels |
Rocket | Atlas V |
Mission Duration | 2006 - ongoing |
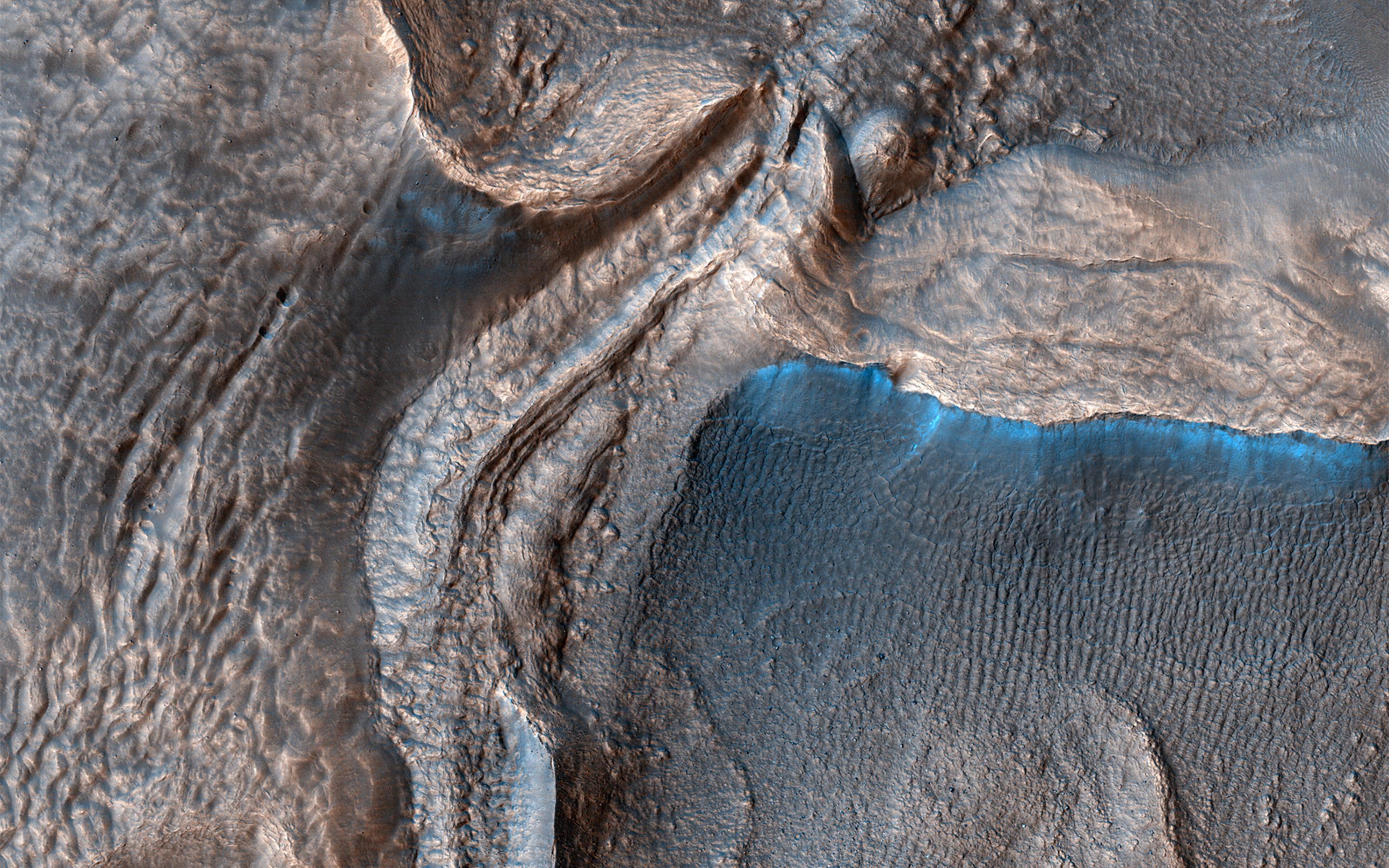

Studying the History of Water on Mars
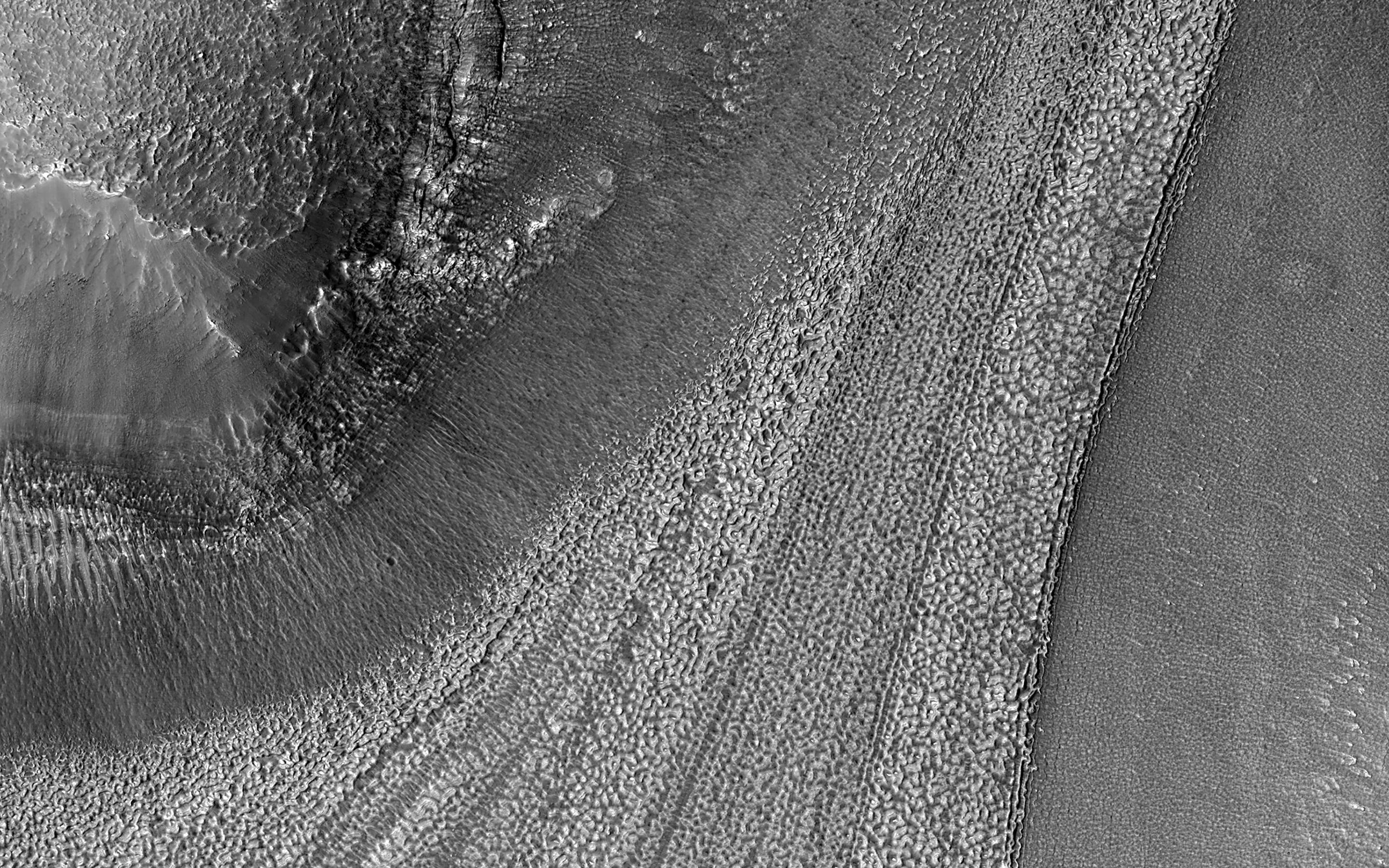
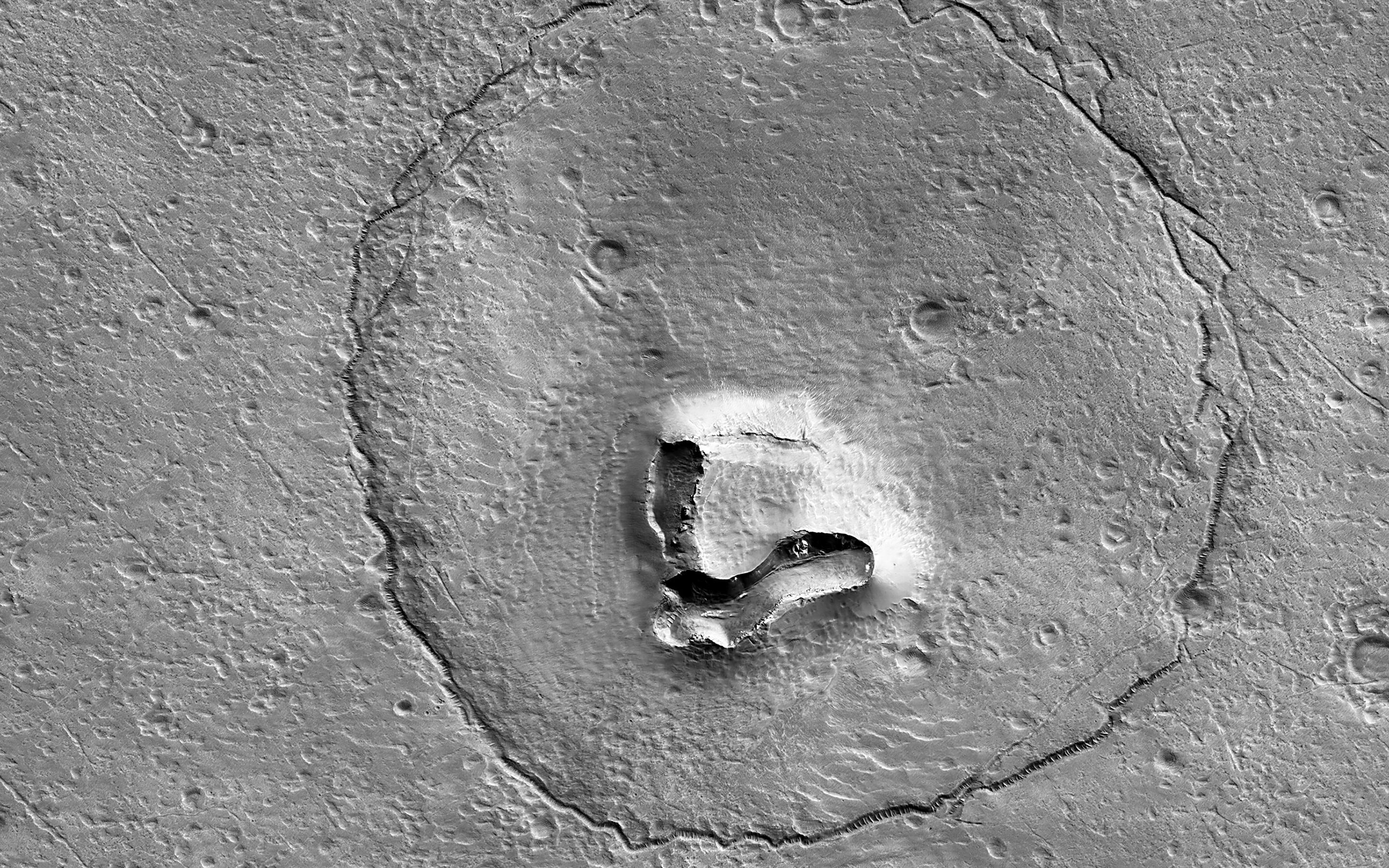
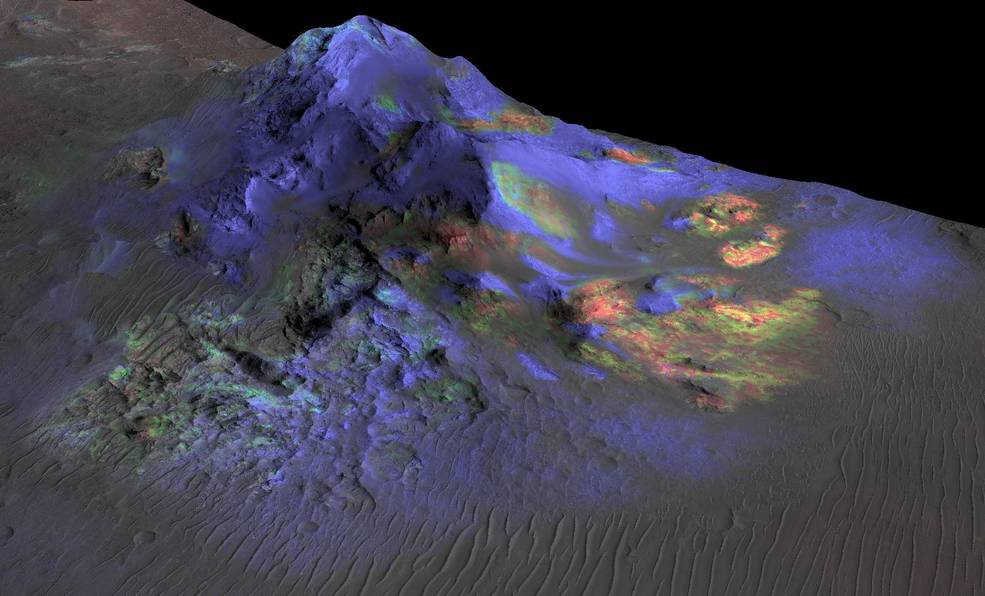
After a seven-month cruise to Mars and six months of aerobraking to reach its science orbit, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter began seeking out the history of water on Mars with its science instruments. The instruments zoom in for extreme close-up photography of the martian surface, analyze minerals, look for subsurface water, trace how much dust and water are distributed in the atmosphere, and monitor daily global weather.These studies are identifying deposits of minerals that may have formed in water over long periods of time, looking for evidence of shorelines of ancient seas and lakes, and analyzing deposits placed in layers over time by flowing water. The mission is examining whether underground martian ice discovered by the Mars Odyssey orbiter is the top layer of a deep ice deposit or a shallow layer in equilibrium with the atmosphere and its seasonal cycle of water vapor.
Looking at Small-Scale Features
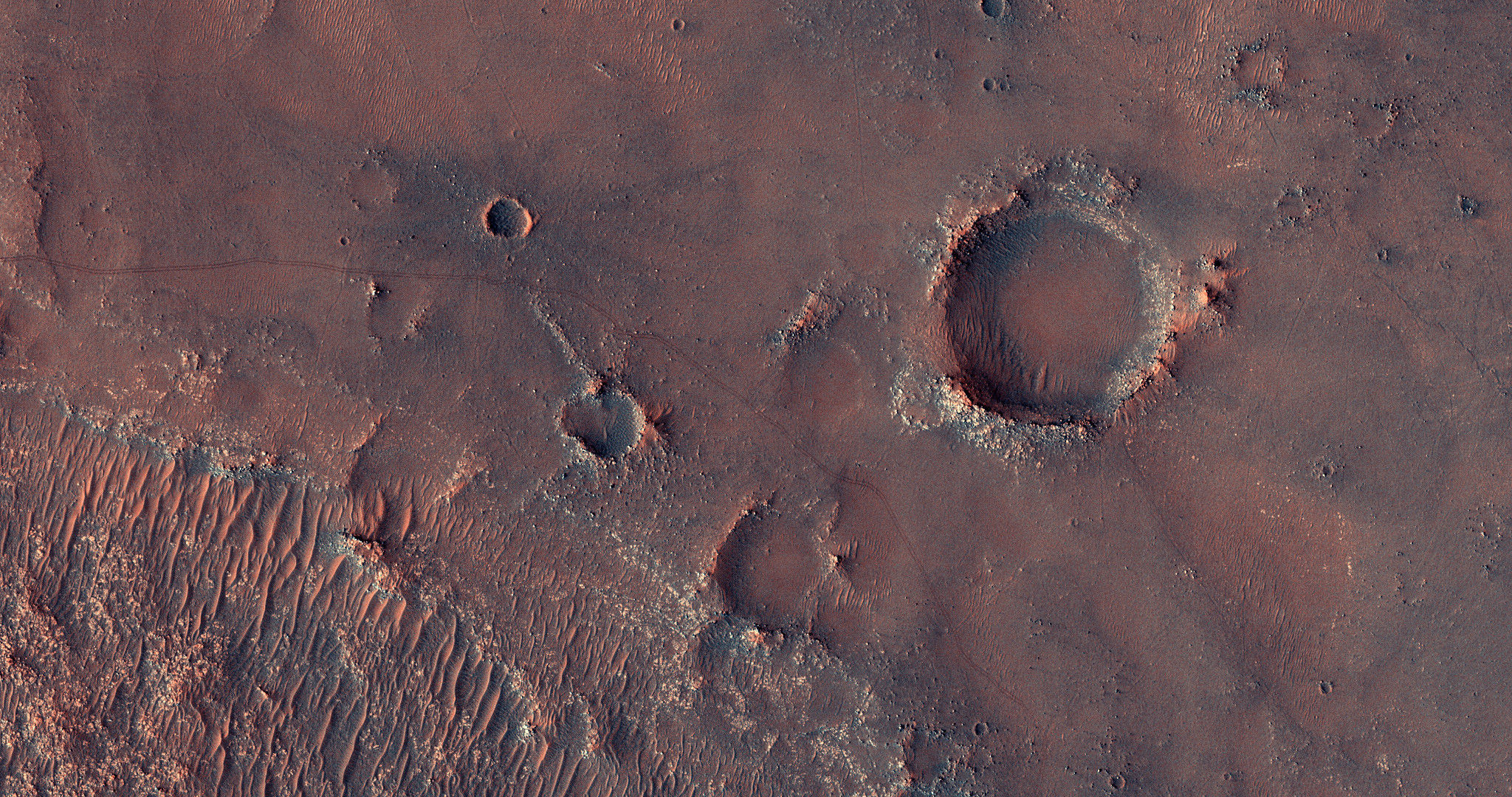
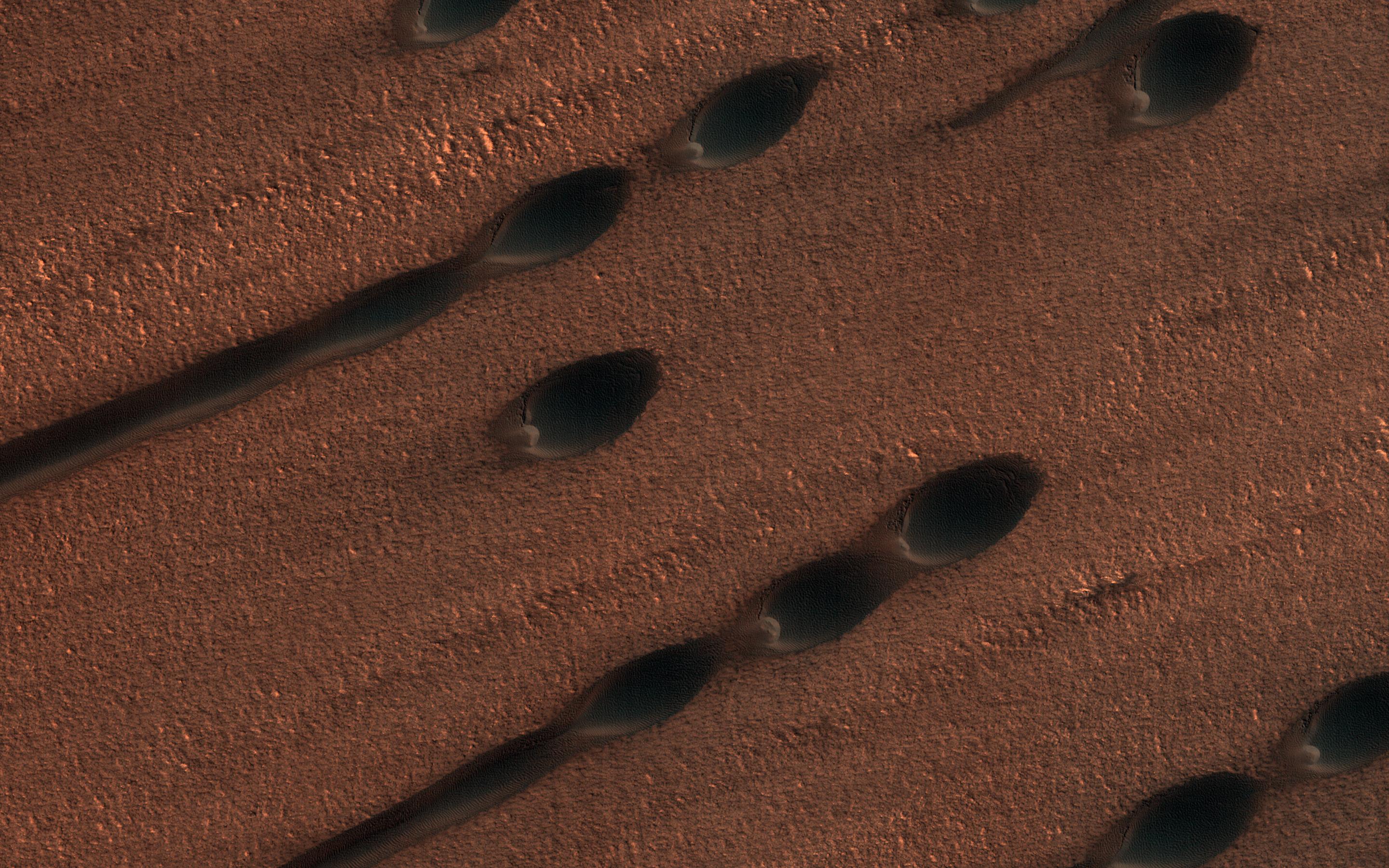
In its survey of the red planet, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is increasing tenfold the number of spots surveyed close-up. One of the orbiter's cameras is the largest ever flown on a planetary mission. Though previous cameras on other Mars orbiters could identify objects no smaller than a school bus, this camera can spot something as small as a dinner table. That capability has allowed the orbiter to identify obstacles such as large rocks that could jeopardize the safety of landers and rovers, including the Phoenix mission and Mars Science Laboratory mission. Its imaging spectrometer looks at small-scale areas about five times smaller than a football field, a scale perfect for identifying any hot springs or other small water features.

The Interplanetary Internet
The orbiter's telecommunications systems provide a crucial service for Martian spacecraft, serving as the first link in a communications bridge back to Earth, an "interplanetary Internet" that can be used by numerous international spacecraft in coming years.
Learn More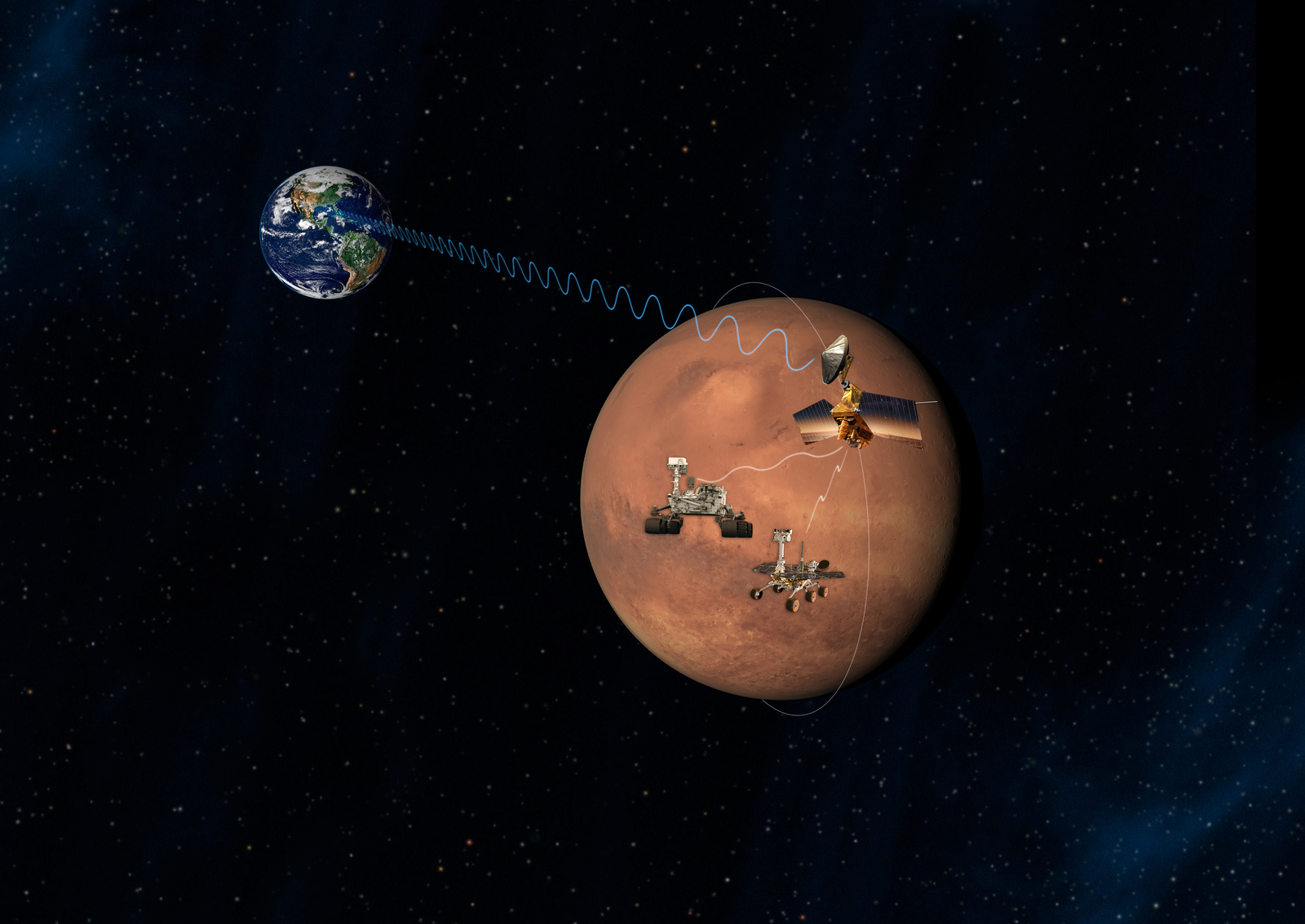
Science
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is providing new information in unprecedented detail about the surface, subsurface, and atmosphere of Mars.
Learn More